This document describes the process of installing Openfiler using the
default graphical installation interface. If you experience any
problems with the graphical install track, such as a garbled screen due
to the installer not being able to auto-detect your graphics hardware,
please try a text-based install. The text-based install track is
described
here.
Total time for installation is about 15 - 20 minutes including software installation to disk.
System Requirements
Openfiler has the following hardware requirements to be successfully installed:
-
x64 based computer with at least 4GB RAM and 12GB storage for the OS image.
-
At least one supported network interface card
-
A CDROM or DVD-ROM drive if you are performing a local install
-
A supported disk controller with data drives attached.
Please see full system requirements information here.
Installation
The installation process is described with screenshots for
illustrative purposes. If you are unable to proceed at any point with
the installation process or you make a mistake, use the Back button to
return to previous points in the installation process. Any errors or
intractable problems with the installation process should be reported
either to the
Openfiler Users mailing list or, alternatively, if you feel you have found a bug please use the
bug tracking system.
If you report a bug, be sure to enter a valid email address so that you
can keep track of any updates to it right up to resolution. You
*must* first register with the
bug tracker in order to be able to
post a new bug.
Starting the Installation
To begin the installation, insert the Openfiler disk into your
CD/DVD-ROM drive and ensure your system is configured to boot off the
CD/DVD-ROM drive. After the system POSTs, the installer boot prompt will
come up. At this point, just hit the Enter key to proceed.
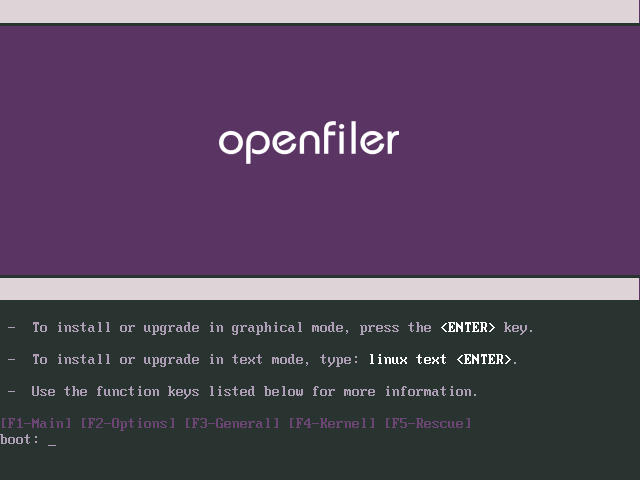
After a few moments, the first screen of the installer will be
presented. If at this point your screen happens to be garbled, it is
likely that the installer has been unable to automatically detect your
graphics subsystem hardware. You may restart the installation process in
text-mode and
proceed accordingly
in that case. The first screen of the installer is depicted below. The
next step is to click on the Next button to proceed with the
installation.
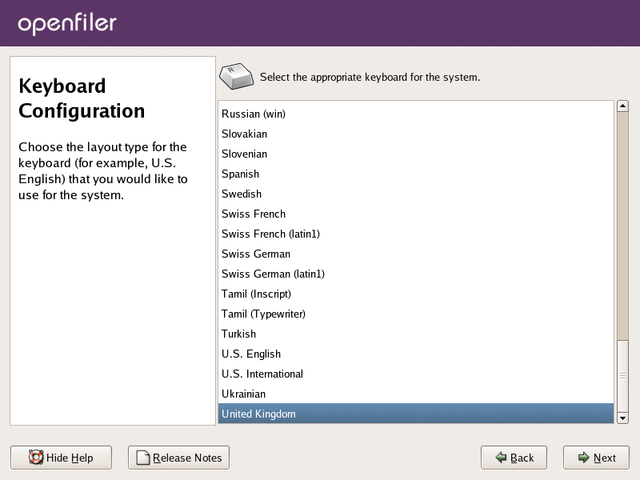
Keyboard Selection
This screen deals with keyboard layout selection. Use the scroll bar
on the right to scroll up and down and select your desired keyboard
layout from the list. Once you are satisfied with your selection, click
the Next button to proceed.
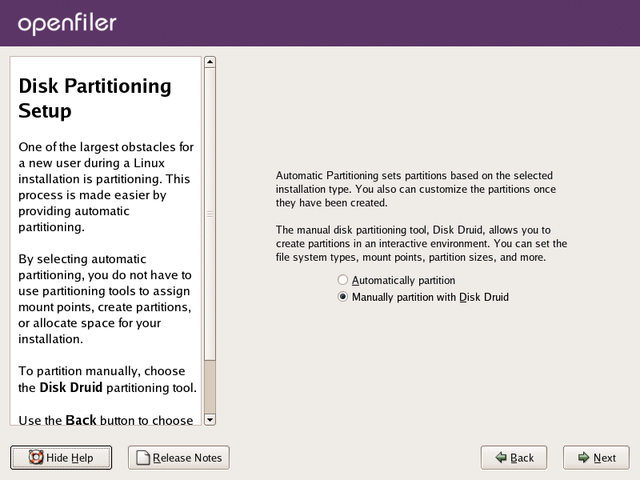
Disk Partitioning Setup
Next comes the disk partitioning. You must select manual disk
partitioning as it ensures you will end up with a bootable system and
with the correct partitioning scheme.
Openfiler does not
support automatic partitioning and you will be unable to configure data
storage disks in the Openfiler graphical user interface if you select
automatic partitioning. Click the Next button once you have selected the correct radiobutton option.
Disk Setup
On the disk setup screen, if you have any existing partitions on the system, please delete them.
DO NOT DELETE ANY EXISTING OPENFILER DATA PARTITIONS UNLESS YOU NO LONGER REQUIRE THE DATA ON THEM.
To delete a partition, highlight it in the list of partitions and click
the Delete button. You should now have a clean disk on which to create
your partitions.
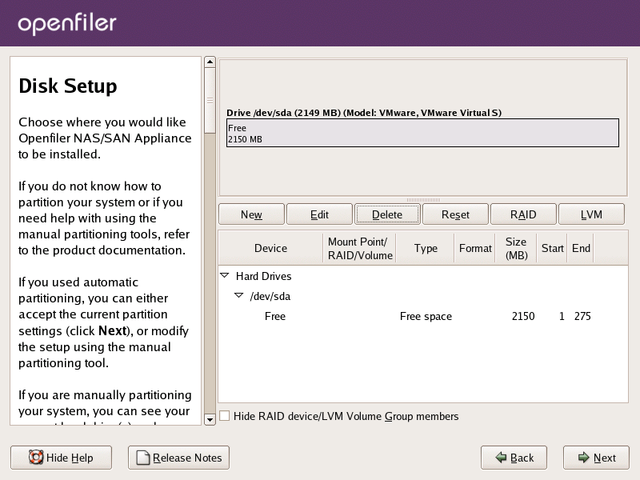
You need to create three partitions on the system in order to proceed with the installation:
-
"/boot" - this is where the kernel will reside and the system will boot from
-
"swap" - this is the swap partition for memory swapping to disk
-
"/"- this is the system root partition where all system applications and libraries will be installed
Create /boot Partition
Proceed by creating a boot partition. Click on the New button. You
will be presented with a form with several fields and checkboxes. Enter
the partition mount path "/boot" and the select the disk on with to
create the partition. In the illustrated example, this disk is
hda
(the first IDE hard disk). Your setup will very likely be different as
you may have several disks of different types. You should make sure that
only the first disk is checked and no others. If you are installing on a
SCSI-only system, this disk will be designated
sda. If you are installing on a system that has both IDE and SCSI disks, please select
hda if you intend to use the IDE disk as your boot drive.
The following is a list of all entries required to create the boot partition:
-
Mount Point: /boot
-
Filesystem Type: ext3
-
Allowable Drives: select one disk only. This should be the first IDE (hda) or first SCSI disk (sda)
-
Size(MB): 100 (this is the size in Megabytes, allocate 100MB by entering "100")
-
Additional Size Options: select Fixed Size radiobutton from the options.
-
Force to be a primary partition: checked (select this checkbox to force the partition to be created as a primary partition)
After configuration, your settings should resemble the following illustration:
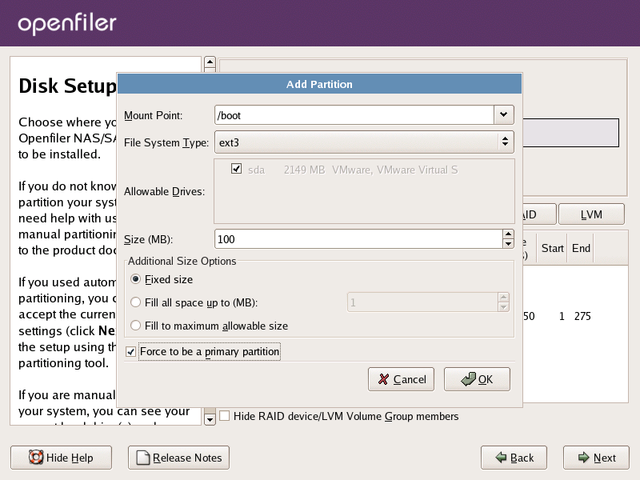
Once you are satisfied with your entries, click the OK button to create the partition.
Create / (root) Partition
Proceed by creating a
root partition. Click on the New
button. You will be presented with the same form as previously when
creating the boot partition. The details are identical to what was
entered for the
/boot partition except this time the Mount Point: should be
"/" and the Size(MB): should be 2048MB or at a minimum 1024MB.
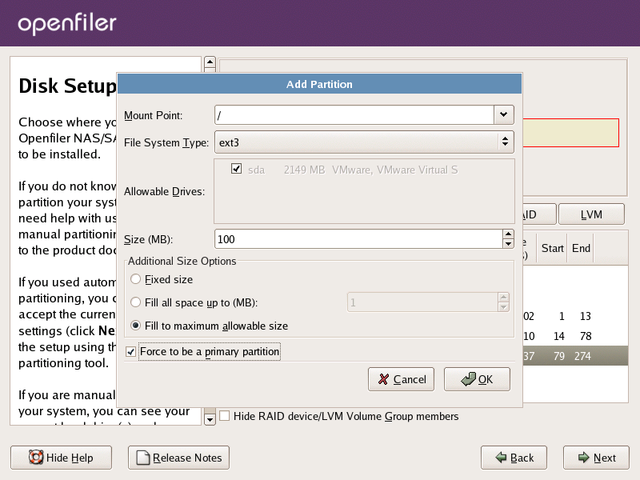
Once you are satisfied with your entries, click the OK button to proceed.
Create Swap Partition
Proceed by creating a
swap partition. Click on the New
button. You will be presented with the same form as previously when
creating the boot and root partitions. The details are identical to what
was entered for the
boot partition except this time the Mount Point: should
swap.
Use the drop down list to select a swap partition type. The Size(MB):
of the partition should be at least 1024MB and need not exceed 2048MB.
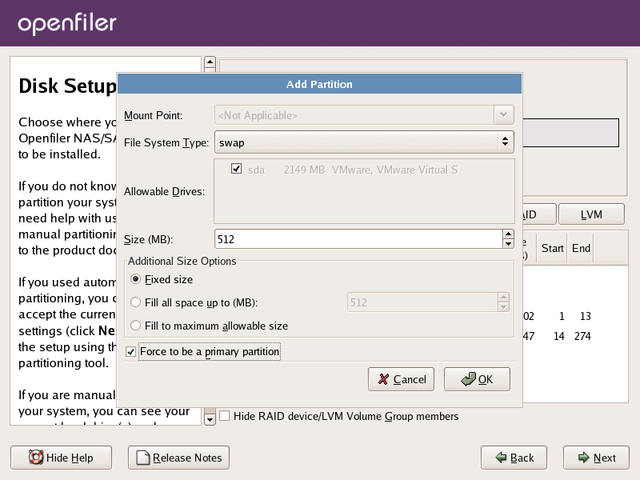
Once
you are satisfied with your entries, proceed by clicking the OK button
to create the partition. You should now have a set of partitions ready
for the Openfiler Operating System image to install to. Your disk
partition scheme should resemble the following:
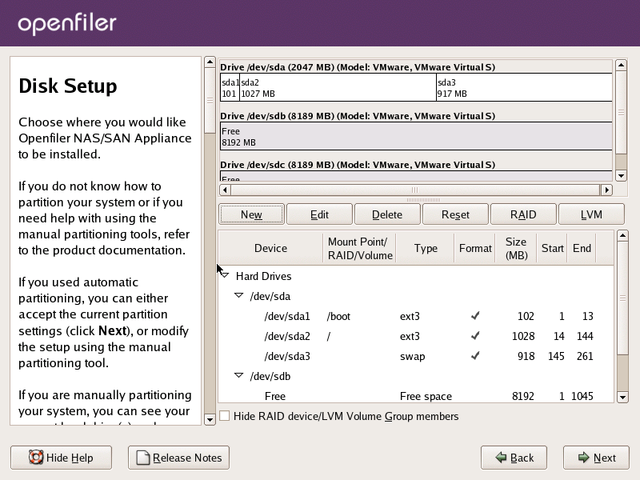
You have now completed the partitioning tasks of the installation process and should click Next to proceed to the next step.
Network Configuration
In this section you will configure network devices, system hostname
and DNS parameters. You will need to configure at least one network
interface card in order to access the Openfiler web interface and to
serve data to clients on a network. In the unlikely event that you will
be using DHCP to configure the network address, you can simply click
Next and proceed to the next stage of the installation process.
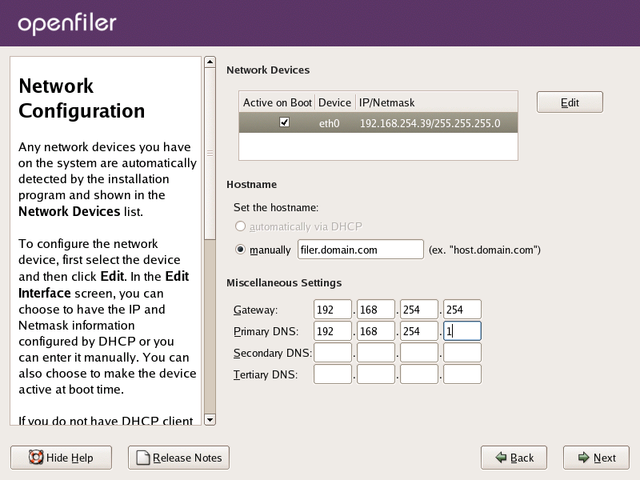
If on the other hand you wish to define a specific IP address and
hostname, click the Edit button at the top right corner of the screen
in the Network Devices section. Network interface devices are designated
eth
X where
X is a number starting at 0. The first network interface device is therefore
eth0. If you have more than one network interface device, they will all be listed in the Network Devices section.
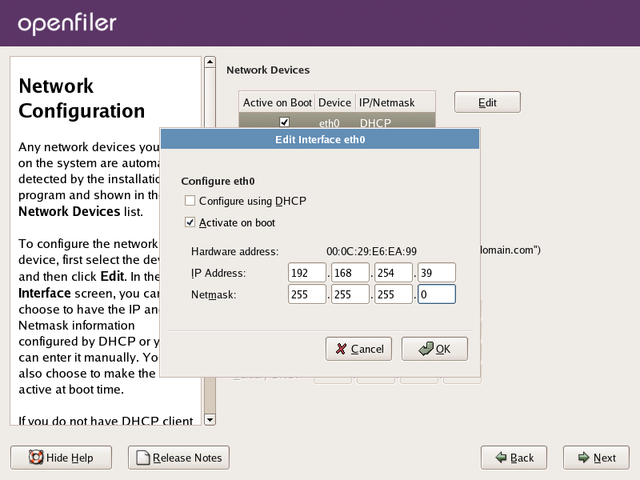
When you click the Edit button, a new form will popup for you to
configure the network device in question. As you do not wish to use DHCP
for this interface, uncheck the Configure Using DHCP checkbox. This
will then allow you to enter a network IP address and Netmask in the
appropriate form fields. Enter your desired settings and click OK to
proceed.
Once you have configured a network IP address, you may now enter a hostname for the system. The default hostname
localhost.localdomain
is not suitable and you will need to enter a proper hostname for the
system. This will be used later when you configure the system to
participate on your network either as an Active Directory / Windows NT
PDC client or as an LDAP domain member server. You will also, at this
point, need to configure gateway IP address and DNS server IP addresses.
To complete this task you will need the following information:
-
Desired hostname - this is the name you will call the system. Usually
this will be a fully qualified hostname e.g homer.the-simpsons.com .
-
Gateway IP address - this is the IP address of your network gateway to allow routing to the Internet
-
Primary DNS Server - this is the DNS server on your network. Note
that if you intend to use Active Directory or LDAP as your
authentication mechanism, you will need to assign a functional DNS IP
address so that the authentication mechanism is able to resolve the
authentication server hostnames.
-
Secondary/Tertiary DNS Server - enter a second and third DNS server if they are available on your network.
The following illustration shows an example where a hostname has
been assigned, and gateway IP, primary and secondary DNS information
has also been entered.
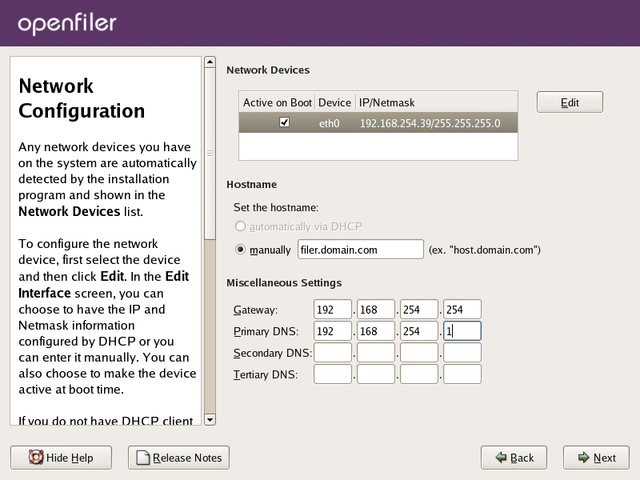
Once you are satisfied with your entries, please proceed by clicking the Next button.
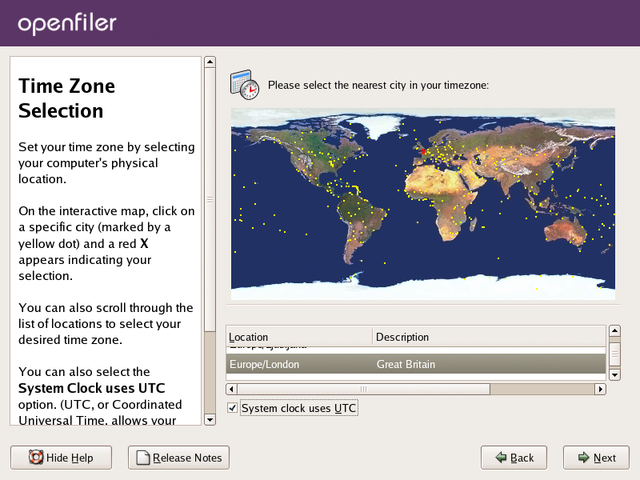
Time Zone Selection
Set the default system time zone. You can achieve this by following
the instructions on the left side of the screen. If your system BIOS has
been configured to use UTC, check the UTC checkbox at the bottom of the
screen and click Next to proceed.
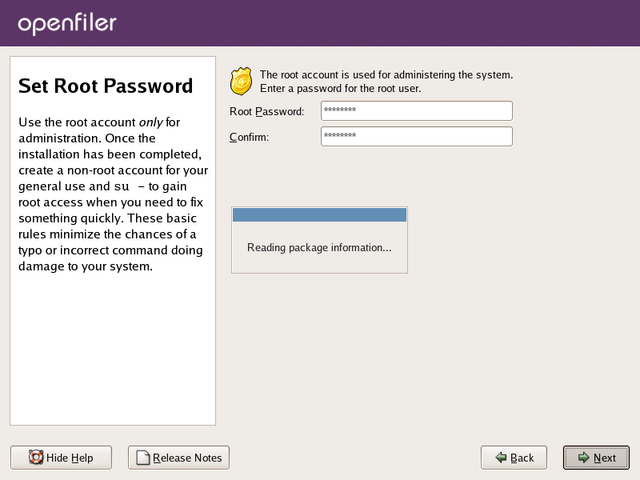
Set Root Password
You need to configure a root password for the system. The root
password is the superuser administrator password. With the root account,
you can log into the system to perform any administrative tasks that
are not offered via the web interface. Select a suitable password and
enter it twice in the provided textboxes. When you are satisfied with
your entries, click Next to proceed with the installation process.
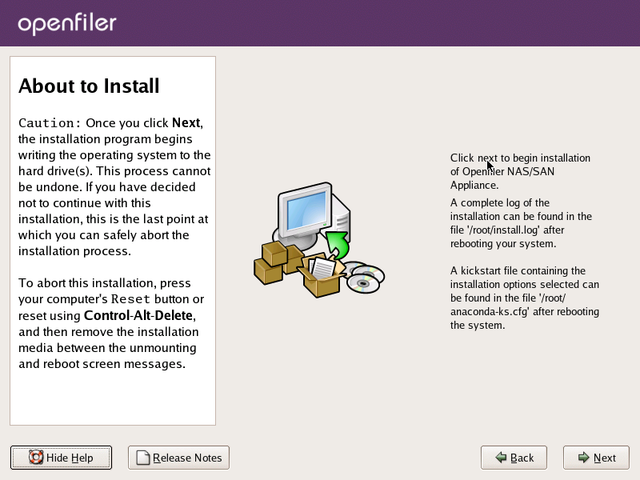
About To Install
This screen informs you that installation configuration has been
completed and the installer is awaiting your input to start the
installation process which will format disks, copy data to the system
and configure system parameters such as setting up the boot loader and
adding system users. Click Next if you are satisfied with the entries
you have made in the previous screens.
Note
You cannot go back to previous screens once you have gone past this
point. The installer will erase any data on the partitions you defined
in the partitioning section.
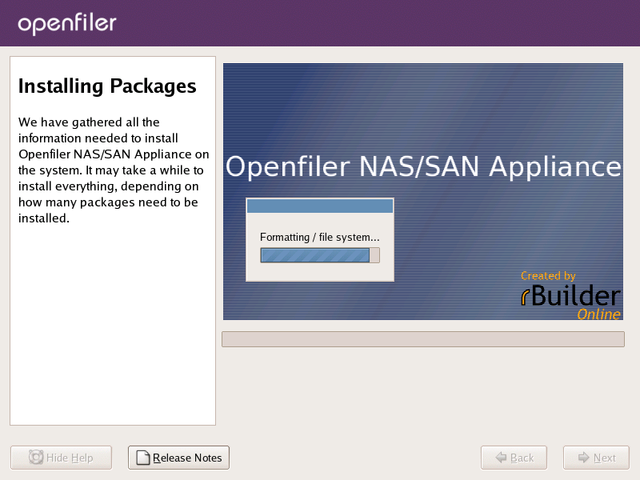
Installation
Once you have clicked Next in the preceding section, the installer
will begin the installation process. The following screenshots depict
what happens at this point.
Installation Complete
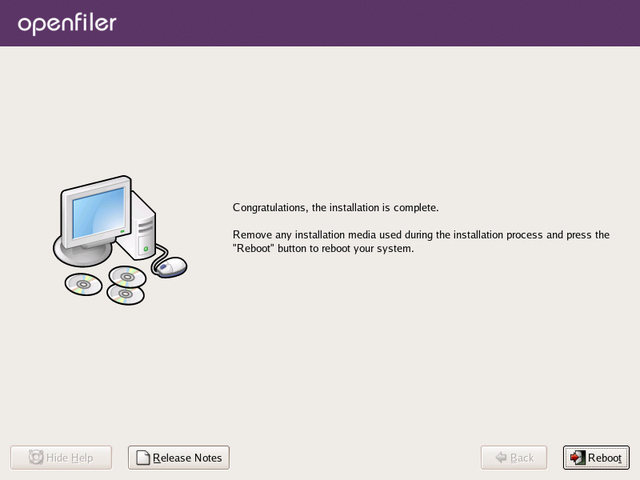
Once the installation has completed, you will be presented with a
congratulatory message. At this point you simply need to click the
Reboot button to finish the installer and boot into the installed
Openfiler system.
Note
After you click Reboot remove the installation CD from the CD/DVD-ROM drive.
Once
the system boots up, start configuring Openfiler by pointing your
browser at the host name or IP address of the Openfiler system. The
interface is accessible from https port 446. e.g..
Management Interface: https://:446
Administrator Username: openfiler
Administrator Password: password
You can learn how to manage the Openfiler system by browsing the administrator guide online which can be found.
Source :
https://www.openfiler.com
Published By
S.G.Godwin Dinesh.MCA
Sr.System Adminstrator